2022 / 11 / 18
Differences between twin-screw extruders and single-screw extruders in PVC processing

Twin-screw extruder is the most common machinery in the modified plastics industry, widely used in the polymer processing industry and other production and processing areas; Twin-screw extruder variety, can be divided into two major categories of engaging and non-engaging, engaging twin-screw extruder can be divided into two major categories of isotropic and heterotropic rotation.
Difference in working principle between coaxial twin-screw extruder and single-screw extruder
The structure and function of isotropic twin-screw extruder is very similar to that of single-screw extruder, but there are great differences in the working principle. Mainly in the following aspects:
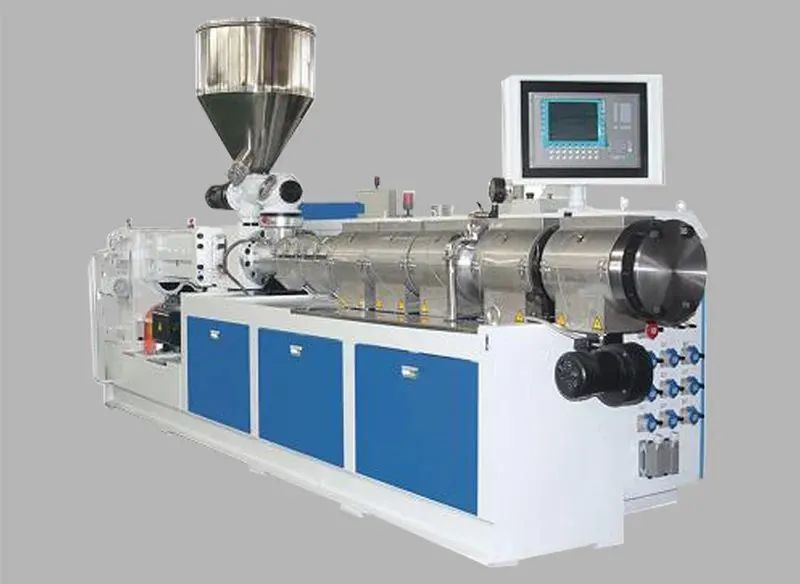
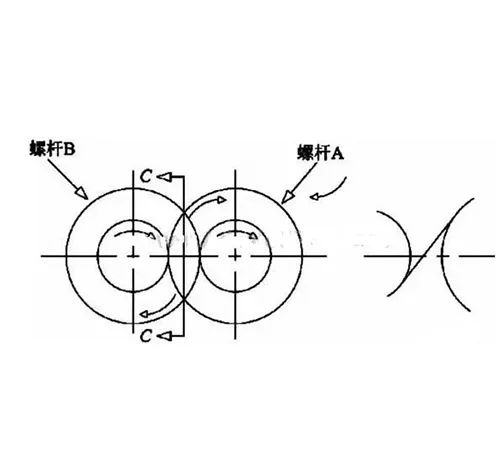
(1) forced transportation. Engage the same direction of rotation of the twin-screw, in the engagement of the two screws in the opposite direction of the speed of movement, a screw to pull the material into the mesh gap, and the other screw to push out the material from the gap, the result is that the material from one screw slot to another screw slot, the material along the screw was “∞” shaped to the direction of the machine head to be forced to transport.
(2) homogenization and mixing. Isotropic rotating twin-screw in the engagement at the gap is very small, screw prongs and screw groove speed in the opposite direction, the relative speed is large, so the engagement area has a very high shear speed, shear force is very large, the mixing effect is far better than the single-screw extruder and anisotropic rotating twin-screw extruder.
3) Self-cleaning. Isotropic rotating twin-screw extruder, due to the engagement zone screw prongs and screw groove speed in the opposite direction, the relative speed is large, so it has a fairly high shear speed, can scrape away any accumulation of material adhering to the screw, there is a very good self-cleaning effect, so that the material's residence time is very short, and it is not easy to produce localized degradation of the deterioration.
(4) Plasticization of materials. The size of the screw gap has a great impact on the quality of material plasticization. The smaller the gap, the greater the shear force, but the amount of material through the decrease; the larger the gap, the amount of material through the increase, but the shear force decreases.
(5) Material compression. Isotropic twin-screw extruder compression of the material is much more than the method, the comprehensive effect is good.
(6) Charging method. Coaxial twin-screw extruder requires uniform quantitative feeding, the use of metering hunger feeding method.
(7) exhaust. As a result of starvation feeding, you can use a large lead thread conveying elements, so that the screw groove in the unfilled state at zero pressure state, so that you can set out the exhaust section.

Application of twin-screw extruder
Twin-screw extruder can be divided into anisotropic twin-screw and isotropic twin-screw according to the difference of the direction of rotation of the two screws.
The meshing co-rotating twin-screw extruder is widely used in the physicochemical modification of matrix resin, such as filling, reinforcing, toughening, reaction extrusion, and so on.
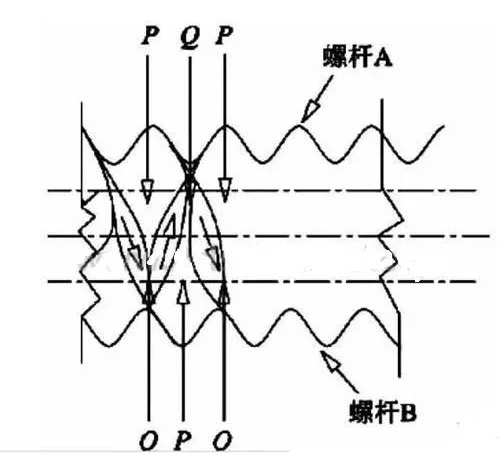
With a variety of raw materials dispersed mixing-based mixing should be used isotropic twin-screw extruder, and the above figure shows the speed vector of the isotropic twin-screw into each other in reverse, so the isotropic rotation of the twin-screw and isotropic rotation of the twin-screw compared to the shear effect of its much larger, unsuitable for the mixing and molding of PVC.
Commonly used in blended filler plastics is powdered calcium carbonate, talcum powder, titanium dioxide, general filler amount of 30% to 60%, filler masterbatch up to 80%. As the powdered filler contains a large amount of air, in the screw kneading area of the mixing air will be separated out, resulting in the reverse flow of materials into the screw groove, affecting the positive conveyance of the powder, and ultimately reduce the amount of extrusion.
Application examples of twin-screw extruder: glass fiber reinforced, fuel-retardant granulation (such as PA6, PA66, PET, PBT, PP, PC enhanced flame retardant, etc.); high filler granulation (such as PE, PP filled with 75% CaCO3.); heat-sensitive materials pelletizing (such as PVC, XLPE cable materials); thick color masterbatch (such as 50% filled with pigmented powder); anti-static masterbatch, alloys, color, low filler blending granulation; cable materials; cable materials; cable materials; cable materials. Filling co-blending granulation; cable material granulation (such as sheath material, insulation material); XLPE pipe material granulation (such as masterbatch for hot water cross-linking); thermosetting plastics mixing and extrusion (such as phenolic resins, epoxy resins, powder coatings); hot-melt adhesive, PU reaction extrusion granulation (such as EVA hot-melt adhesive, polyurethane); K resins, SBS de-volatilization granulation and so on.

Advantages and disadvantages
Due to the complexity of the structural design and processing of the twin-screw extruder, the theoretical development is not perfect, but the combined design of the isotropic twin-screw extruder can be arranged and combined with a variety of geometrical shapes of the threaded elements and barrel elements, and according to the experience-theoretical-practical-inspection, so that it can be optimized for the different mixing requirements to adapt to the needs of different process formulas, which makes the isotropic twin-screw extruder has a very strong Adaptability. Mainly in the following aspects:
(1) mixing performance: as the two screws engage with each other, and can be added according to the need for a variety of threaded elements, such as anti-threaded elements, engaging disk elements, toothed disk elements, etc., to precisely regulate the shear/mixing, so that the mixing intensity and quality of mixing (whether distributed or dispersed mixing) can be effectively controlled. This is a single-screw extruder can not reach.
(2) Processing flexibility: co-rotating twin-screw extruder usually adopts the metering hunger feeding, output depends on the amount of feeding, independent of the screw speed, is an independently controllable variable, and thus can be flexibly dealt with in a machine with a variety of processing functions, such as melting, mixing, exhausting, reacting and so on.
(3) Controllability of Process Parameters: With narrow residence time distribution, better convection heat transfer and precisely controlled temperature profile, the coaxial twin-screw extruder can get better shear-time-temperature history in extrusion, and input mechanical energy in a wider range, so that it can get better product quality stability.
(4) Higher efficiency of process production: the positive displacement conveying action of the screw can handle a wider variety of raw materials and mixed formulations with shorter downtime.
(5) Higher economy: due to the high process flexibility and productivity, a wider range of end products can be produced with a high degree of consistency in product quality, and screw wear can be compensated for by the adjustment of screw speed.

Key differences between an anisotropic twin-screw extruder and a single-screw extruder
What is the input principle of an anisotropic twin-screw extruder?
In an anisotropic twin-screw extruder, the material is conveyed with a positive displacement similar to that in a gear pump. Anisotropic twin-screw extruder has a low rotational speed, low shear heat generation of the material, and the material is not easy to decompose, so it does not require high thermal stability of the material, and it is especially suitable for molding and processing of heat-sensitive materials (e.g., PVC). Compared with the isotropic twin-screw extruder, the isotropic twin-screw extruder has higher conveying efficiency, better exhaust effect and melting effect, although the material dispersion and mixing effect is poorer than that of the isotropic twin-screw extruder, but the ability to establish a stable pressure in the head is stronger, and therefore it is more suitable for extruding products directly. In addition to the use of anisotropic twin-screw extruder instead of a single-screw extruder, you can eliminate the pre-plasticization granulation process, direct extrusion processing of PVC powder, so that the cost of products down. Anisotropic rotary twin-screw extruder is mainly used for extruding PVC pipes. Profiles, plates and pelletizing. Parallel anisotropic twin-screw extruder has also begun to be used in large-scale HDHDPE pipe production line.
Anisotropic conical twin-screw extruder is traditionally used in the extrusion of PVC products, but in recent years there have been domestic examples of the application of anisotropic conical twin-screw extruder to the extrusion of polyolefin pipes, and practice has shown that it has been largely successful. The purpose of this practice is to save energy. A 65 body 132umum conical twin-screw extruder, drive motor power is only 37kW, in the extrusion of polyethylene pipe, pipe specifications and output can be equivalent to a 75mm or even 80mm single-screw extruder, and generally a 75mm or 80mm single-screw extruder, the drive power of the least is 90kW. foreign countries already have a ready-made parallel anisotropic twin-screw extruder extrusion products mature. Foreign countries already have mature experience in extruding products with parallel anisotropic twin-screw extruder, the domestic alternative to use anisotropic conical twin-screw extruder in fact, or for the consideration of the cost of the equipment, parallel anisotropic twin-screw extruder manufacturing costs higher than that of the anisotropic conical twin-screw extruder.
This method of use is certainly not a simple alternative, after all, polyethylene melt and PVC melt flow performance has obvious differences, so for the extrusion of PVC products for the anisotropic conical twin-screw extruder, the need to redesign the screw can be used for the extrusion of polyethylene; and the head should also be modified accordingly. In recent years, some people try to extrude products with isotropic twin-screw extruder (including conical twin and flat twin), and some progress has been made, but I think that from the point of view of energy saving, there is no great difference between isotropic and anisotropic twin-screw, and it is more difficult for isotropic twin-screw extruder to establish a stable pressure of the head, which is not as easy as adopting anisotropic twin-screw directly.
The main differences between anisotropic twin-screw extruder and single-screw extruder are the following two points:
1) Their conveyor mechanisms are different. Single-screw extruder in the material transportation is drag type flow, solid transportation process for friction drag, melt transportation process for viscous drag, the size of the friction factor between the solid material and the metal surface and the viscosity of the melt material, to a large extent, determines the size of the single-screw extruder conveying capacity. The conveying of material in anisotropic twin-screw extruder is positive displacement conveying, with the rotation of the screw, the material is
With the rotation of the screw, the material is pushed forward compulsorily by the intermeshing threads, and its positive displacement conveying capacity depends on the proximity of the screw prong of one screw to the screw dregs of the other screw. The maximum positive displacement conveyance can be obtained by using closely meshed anisotropic rotating twin-screw extruder.
2) The velocity fields of the two are different. While the velocity distribution in a single-screw extruder is relatively well defined and easy to characterize, the situation in a twin-screw extruder is quite complex and difficult to characterize. This is mainly due to the fact that there is an engaging zone in the twin-screw extruder, and the complex flow that occurs in the engaging zone makes the twin-screw extruder have many advantages such as adequate mixing, uniform heat transfer, strong melting capacity, good exhaust performance, etc. However, it is difficult to accurately analyze the flow state in the engaging zone.

You May Be Interested
Breaking 3 Technical Barriers! How Rallychem Redefines Premium PVC Transparent Shrink Film Solutions
2025 / 04 / 23
RL-1116S Polyester Wax: Solve SPC Ultra-Thick Board (6mm) Lubrication Challenges
2025 / 02 / 28
Comprehensive analysis of traditional PVC toughening agent: chlorinated polyethylene (CPE)
2025 / 01 / 26
Analysis of Plasticization Issues in PVC Pipes: Improving Production Quality and Efficiency
2025 / 01 / 26
Optimizing the production process of PVC conduit: improving surface smoothness and product competitiveness
2025 / 01 / 26


Whats App

For Inquiries Please Call
Rallychem Will Be Happy To Assist You!

+86 13456396233


info@rallychem.com